Web security 101: Learn how to defend against XSS and how to find it!
Posted on December 5, 2022 • 3 min read • 427 words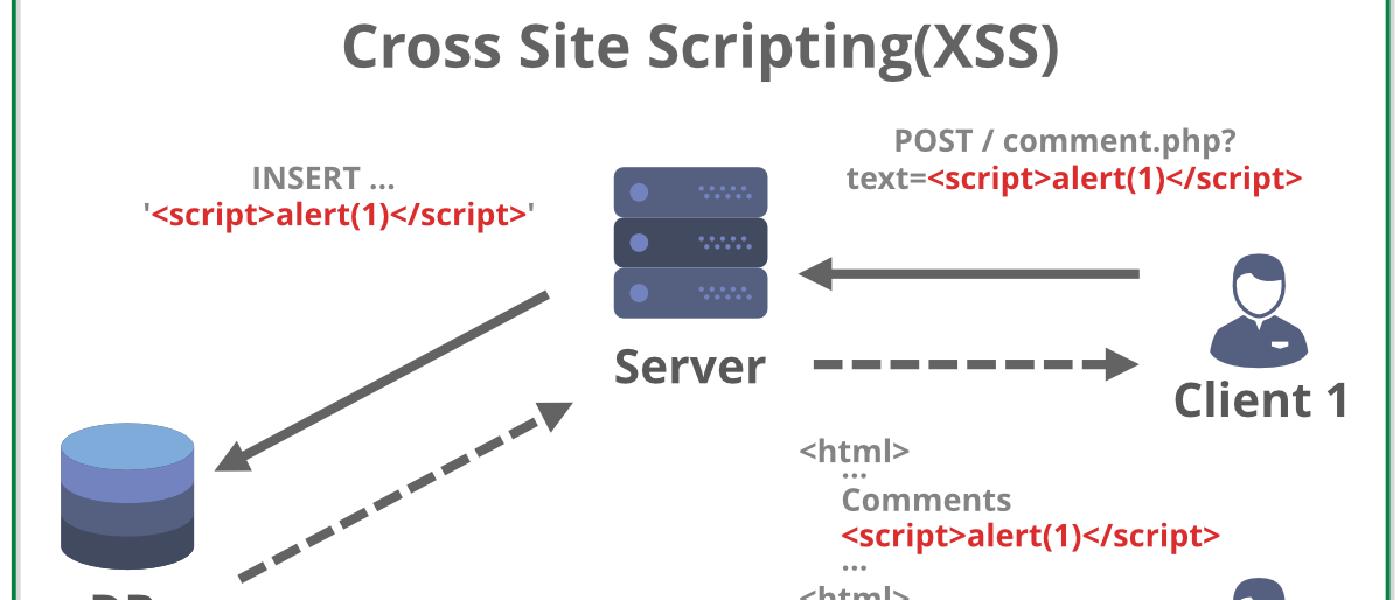
What is XSS?
XSS is an attack on your website in which malicious code is injected into one of your website’s parameters.
Simply you can think of it as a way in which a user can use your website as a command line.
Why is it dangerous?
XSS is a very risky vulnerability in services that allow a user to create and share content. In these cases, an attack may steal data from normal users and use it in malicious ways. And for any hacker, the easiest way to access and the most overlooked part is the website’s interface and how users interact with it.
Example
const [website, setWebsite] = useState()
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<h1>Please enter your website</h1>
<input id="search" onChange={(e) => setWebsite(e.target.value)} placeholder='SafeSaaS'></input>
<a style={{ color: 'white'}} href={website}>Here is my website</a>
</header>
</div>
);
Imagine that instead of
alert('this is XSS'); we can steal the cookie of a user and use it in our stuff.(wanna learn more? see this)
What is vulnerable?
Well, the good news is that most of the available frontend frameworks do automatically escape(filter) JS. So, if you are using react, vue, etc. you should be good to go, just be careful when doing react dynamic hrefs, and dangerouslySetInnerHTML and bypassSecurityTrustAs in Angular. There are vulnerable to XSS.
The bad news is that if you are using vanilla JS, there is a good chance you are vulnerable to XSS.
JS does not escape any inputs and it is extremely easy to exploit XSS.
Types of XSS
- Stored XSS
- Reflected XSS
- DOM-Based XSS
Stored XSS
Stored or Persistent XSS happens when the attackers store the data somewhere and it remains there, like comments, blogs, descriptions.
This can be avoided by implementing a Content Security Policy
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self' example.com *.example.com
Or you can escape the HTML chars:
| Character | Replacement |
|---|---|
& | & |
' | ' |
< | < |
> | > |
Reflected XSS
As in its name, the XSS is reflected on the page after being injected. This is commonly exploited by a malicious link (query), in which the victim is tricked into clicking it.
http://example.com/search.html?query=<script>alert(‘this is XSS’);</script>
DOM XSS
DOM-XSS is normally found on the client side, the difference between DOM-XSS and reflected/stored is that dom XSS is a browser-side injection and is injected in the runtime and the others are server-side
Conclusion
XSS is an easy-to-overlook threat because modern frameworks stop it automatically, but sometimes the default protection is not enough. If you implement a Content-Security-Policy and you make sure that inputs are escaped, you are good to go!
Follow us on Twitter